Lambda was proposed by Nathan Marz based on his experience on distributed data processing systems at Backtype and Twitter.
A generic, scalable, and fault-tolerant data processing architecture.
Lambda Architecture
The aim of Lambda architecture is to satisfy the needs of a robust system that is fault-tolerant, both against hardware failures and human mistakes being able to serve a wide range of workloads and use cases in which low-latency reads and updates are required.
The resulting system should be linearly scalable, and it should scale out rather than up.
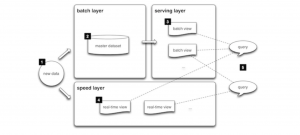
Basic Flow of event:
- All data entering the system is dispatched to both the batch layer and the speed layer for processing.
- The batch layer has two functions:
- managing the master dataset (an immutable, append-only set of raw data)
- to pre-compute the batch views.
- The serving layer indexes the batch views so that they can be queried in low-latency, ad-hoc way.
- The speed layer compensates for the high latency of updates to the serving layer and deals with recent data only.
- Any incoming query can be answered by merging results from batch views and real-time views.
Batch Layer:
- New data comes continuously, as a feed to the data system.
- It gets fed to the batch layer and the speed layer simultaneously.
- It looks at all the data at once and eventually corrects the data in the stream layer.
- Here we can find lots of ETL and a traditional data warehouse.
- This layer is built using a predefined schedule, usually once or twice a day.
- The batch layer has two very important functions:
- To manage the master dataset
- To pre-compute the batch views.
Speed Layer (Stream Layer):
- This layer handles the data that is not already delivered in the batch view due to the latency of the batch layer.
- In addition, it only deals with recent data in order to provide a complete view of the data to the user by creating real-time views.
- The speed layer provides the outputs on the basis enrichment process and supports the serving layer to reduce the latency in responding to the queries.
- As obvious from its name the speed layer has low latency because it deals with the real-time data only and has a less computational load.
Serving Layer:
- The outputs from the batch layer in the form of batch views and from the speed layer in the form of near-real-time views are forwarded to the service layer.
- This layer indexes the batch views so that they can be queried in low-latency on an ad-hoc basis.
Application of Lambda Architecture:
- User queries are required to be served on an ad-hoc basis using the immutable data storage.
- Quick responses are required and the system should be capable of handling various updates in the form of new data streams.
- None of the stored records shall be erased and it should allow the addition of updates and new data to the database.
Pros and Cons of Lambda Architecture:
Pros
- The batch layer of Lambda architecture manages historical data with the fault-tolerant distributed storage which ensures a low possibility of errors even if the system crashes.
- It is a good balance of speed and reliability.
- Fault-tolerant and scalable architecture for data processing.
Cons
- It can result in coding overhead due to the involvement of comprehensive processing.
- Re-processes every batch cycle which is not beneficial in certain scenarios.
- A data modeled with Lambda architecture is difficult to migrate or reorganize.
Thank you for reading. We hope this gives you a brief understanding of the latest news. Are you interested read about other latest technology-related news? Explore our Technology News blogs for more.



